
How Can We Help?
If you need any helps,please feel free to contact us.
What is phlebotomy?
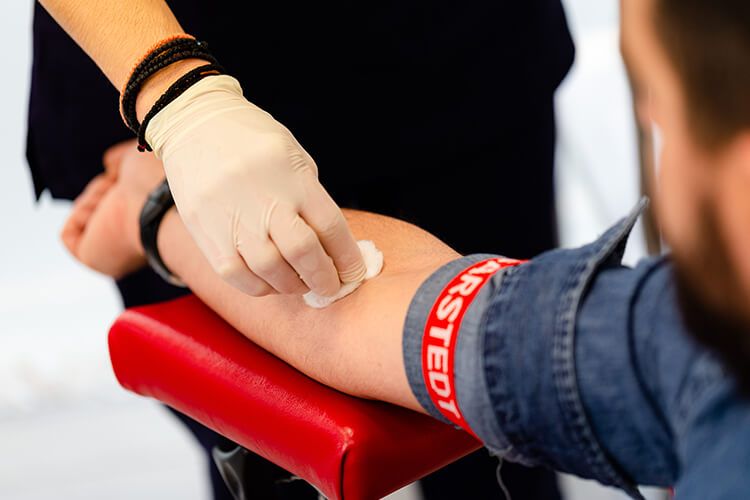
Phlebotomy is the procedure of using a needle to take blood from a vein. It is also known as blood draw, venipuncture,and blood sampling.
During the procedure, specialized phlebotomists collect blood specimens in blood collection tubes, using disposable needles and syringes. The amount of collected blood depends on the type of the diagnostic test.
Venous blood sampling is an important tool for laboratory testing and a necessary step to diagnose many medical conditions.
What are the steps of the phlebotomy procedure?
The phlebotomy procedure is quite simple and is completed within a few minutes. The patient sits on the blood drawing chair and places his hand on the armrest.
The phlebotomist applies a tourniquet in the middle of the patient’s arm and selects the appropriate vein by palpation. Then, he prepares the venipuncture area to ensure aseptic blood sampling.
During the venipuncture procedure, a sterile needle is inserted into the patient’s vein from the inside surface of his elbow.
After taking the sample, the phlebotomist loosens the tourniquet and places a dry cotton ball on the venipuncture site. With gentle movements, he removes the needle and immediately applies constant pressure on the spot for one or more minutes.
The patient stays in the room for a few more minutes to make sure that he feels well. When he is confident that he feels alright, he leaves the diagnostic center.
Pediatric and neonatal blood sampling
PLUS diagnostic center has a well-trained and experienced staff in pediatric and neonatal blood sampling.
The collection of blood is done quickly and painlessly with the use of the appropriate tools. In particular, our phlebotomists use the Vein Viewer Flex device to easily locate the optimal vein puncture site for perfect blood sampling from the first puncture.
Our goal is to make the procedure as enjoyable and stress-free as possible for our little friends and their parents.
Phlebotomy services at PLUS diagnostic center
Using modern venipuncture methods, PLUS diagnostic center collects blood from neonates, children and adults for a wide range of diagnostic services.

Specialized Staff
Blood collection by experienced and fully trained phlebotomists.

Painless Procedure
Small syringe needles and innovative devices for painless blood sampling.

Valid Measurements
High-precision analyzers for reliable results.

Fast Test Results
Flexible delivery of test results at the shortest possible time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Food intake may affect the results of some diagnostic tests. The type of the diagnostic test will determine how many hours before the blood draw you need to fast and whether you should follow any special dietary requirements.
Usually, biochemical tests require an 8-12 hour fasting. You are also advised to avoid consuming fatty meals or alcohol 24 hours before the blood draw.
You may contact our front desk with any questions regarding your preparation before a blood test.
You can drink plain water before a blood test unless your treating physician recommends otherwise. In fact, water consumption is recommended before blood sampling, so that the veins are more prominent.
The answer to that question depends on many parameters that your doctor knows best.
Some medications can affect the metabolism of some substances or the reaction of the analysis. The same applies to dietary supplements or vitamins.
If possible, it is best to avoid taking medication before blood sampling. However, your treating physician is the one who knows your medical history and can advise you on changes in your medication planning.
Phlebotomy during afternoon hours is possible. However, morning blood collection is preferable for most blood tests, especially when fasting is required.
Furthermore, the results of a morning blood sampling are considered more accurate for most measurements. For example, blood iron levels fall by 30% -50% in the afternoon, so morning blood sampling is preferred for Fe measurements.
Smoking can affect the results of blood tests. For this reason, it is preferable to avoid smoking before blood sampling. In fact, in chronic smokers, there is an increase in red blood cells, white blood cells, hemoglobin, and hematocrit.
Blood sampling during menstruation should be avoided. Due to blood loss, the risk of fainting increases. In addition, a few days before and during menstruation, the levels of iron (Fe) in the blood drop. So for more accurate results, especially for a general check-up, you should better wait until the end of your menstruation.